Search across synced data
This tutorial will review how to search across synced third-party Provider data in your Destination.

Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes you have gone through Supaglue's Quickstart using a Postgres Destination that you host and are familiar with the following concepts:
- Postgres
- Postgres JSONB operators
- B-tree and GIN indexes
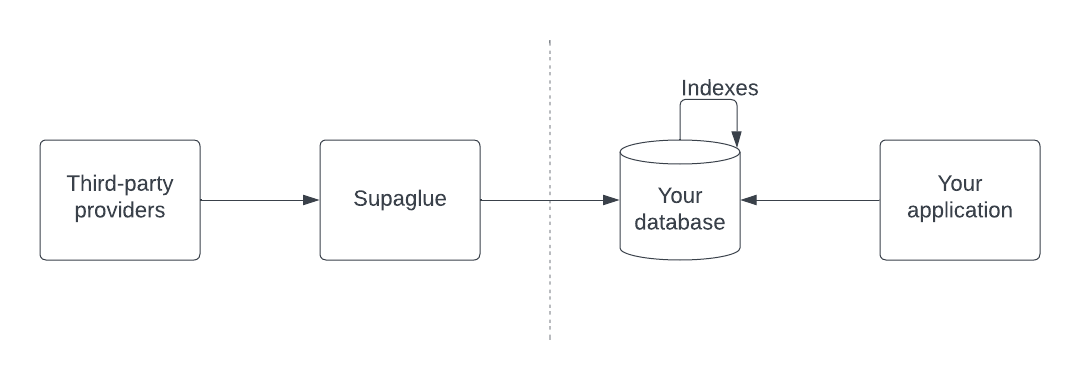
Overview
At this point, you should have third-party Provider data synced to your Postgres database. We'll cover how to use JSONB operators and add indexes to the raw_data JSONB column so you can more efficiently serve queries from it.
JSONB operators
Postgres JSONB operators allow you to query JSONB columns in your Postgres database. There are four ways to access JSONB data:
- Chaining the
->operator - Subscripting
- The
#>operator - Jsonpath
Here are some best practices for when to use each:
- Use the
->operator when you want to access top-level keys in a JSONB object. - Use Subscripting when you're accessing a nested key that is less than seven levels deep.
- Use the
#>operator when accessing a nested key more than seven levels deep. - Generally avoid jsonpath unless you're using a complex query.
Example: -> operator
SELECT raw_data->'name' from "salesforce_Contact";
Example: Subscripting
SELECT raw_data['properties']['associations']['contacts'][0] from "hubspot_company";
Example #> operator
SELECT raw_data#>'{properties,associations,contacts,0}' from "hubspot_company";
Example: Jsonpath
SELECT jsonb_path_query_first(crm_contacts.email_addresses,'$[*] ? (@.email_address_type == "primary").email_address')
info
Read more about the details of JSONB operators here.
JSONB indexes
info
This is under construction.
